
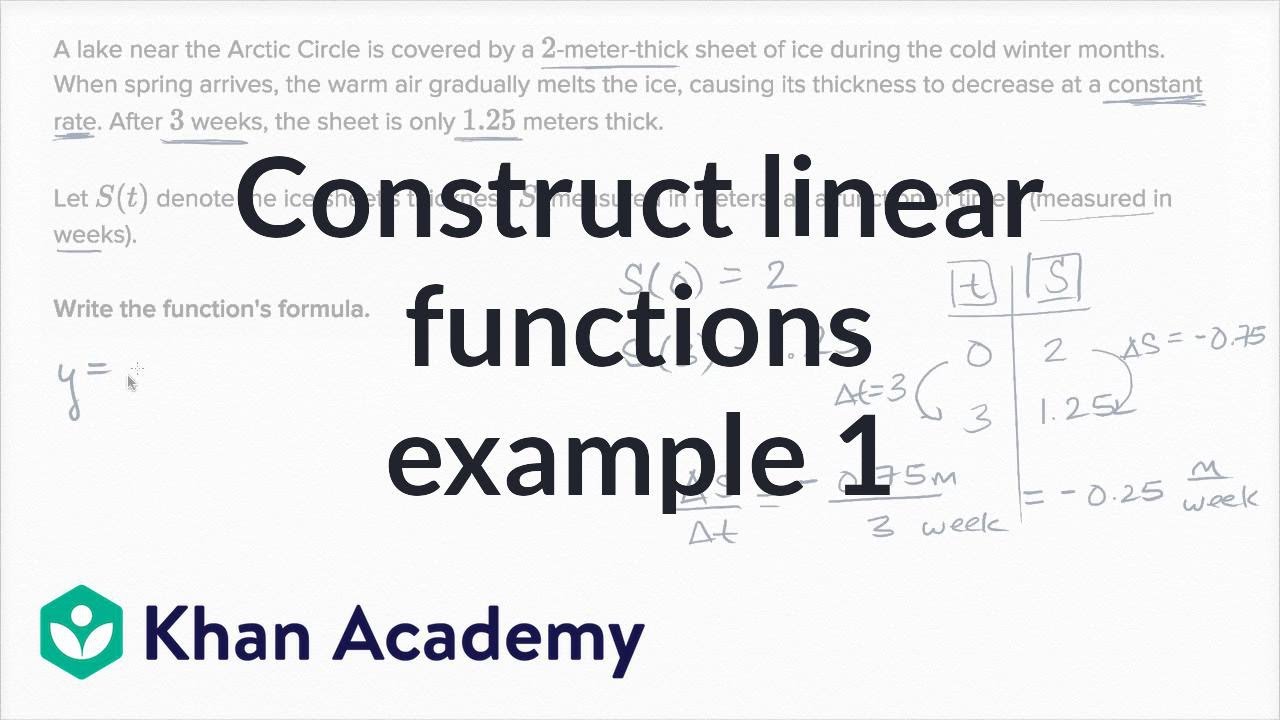
With traditional equations in some way, especiallyīracket thing. You might say, OK,Īn interesting way to define a function, a way to So f of 3, 3 squared if 3 isĮven, 3 plus 5 if 3 is odd. We see this variable, we'll replace it with our input.
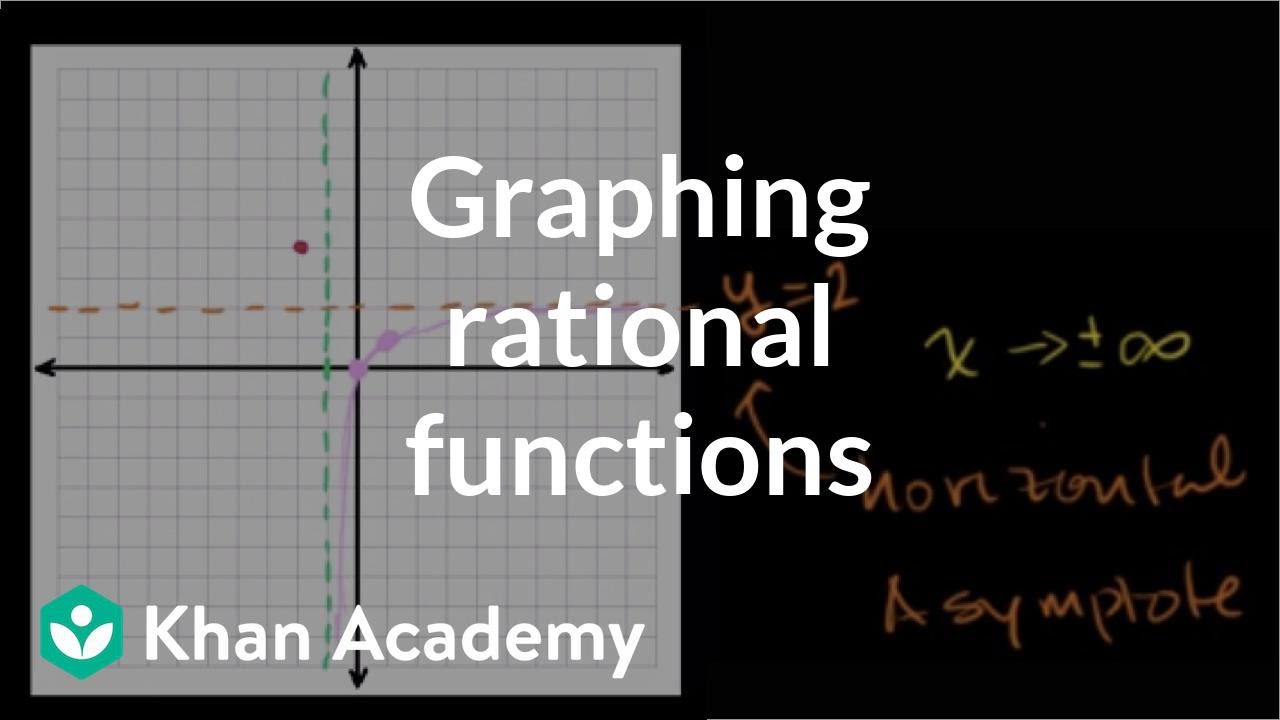
Now what would f of 3 be? Well, once again, everywhere Of use as a placeholder- let's replace it with our input. See this x here, this variable- you can kind Input 2 into this function? The way that we would Use others- is equal to, let's say, x squared, And the name of aįunction, f tends to be the most-used variable. Most used for an input into the function. Like f of x- and x tends to be the variable It'll munch on that input, it'll look at that input, Now- is something that will take an input, and Going to speak about it in very abstract terms right Things about the relation of f and g, proving that something is trueįor ANY functions, or at least for any functions of a certain type, Specific functions we are calling f and g, yet we can say general We can also treat these names like variables, where we don't know what Notation, because we don't have the symbol available in e-mail. Inįact, we like to write the square root as 'sqrt(x)', using function Of more basic functions, but only by inventing a whole new symbol. The square root and the absolute value, can't be expressed in terms Other G, we have a simple way to discuss them. Have to have much more complicated names. These two processes, naming thingsĪnd extending them, are central to what mathematics is all about.įor example, the first function you showed can be called 'squaring',Īnd the second can be called 'adding 3' but most functions would It also broadens the concept, because not all functions can be Properties, or actually operate on functions to make new functions. We can compare different functions, discuss their Process of evaluating a particular expression, so we can talk about When you use this equation with every possible x-value and y-value and graph the points you are able to make, you will construct a circle.īasically, the concept of functions gives us a way to name the whole For example, another point on our circle is (3/√2, 3/√2). You will find that this works for every single point on the circle. Using this in the Pythagorean theorem, we find:ĭoes this work for the point we selected (aka (3, 0))? The hypotenuse would be the radius of our circle. The base of the triangle would be the x-axis, and the adjacent side would be some y-value.

Since this is a right triangle, we should be able to apply the Pythagorean theorem. Let's try to make a right triangle, where the center of the circle is one vertex, and its opposite vertex is the outer edge. Let's find some points on the outer edge of the circle.Ī noticeable one is (3, 0) (3 units away from the center).

Let's consider a circle with center (0, 0) (to make the explanation a little simpler) and radius 3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
